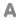Formula : K0.6Mg0.6Al1.4Si4O10(OH)2:2.513H2O
Family:
Space group:
Monoclinic - Prismatic HM symbol (2/m) Space Group: C 2/m
Dana class:
71.3.1b.2VIII- 71 Phyllosilicate Minerals ; 71.3 Phyllosilicates Phyllosilicate Sheets of Six-Membered Rings with 2:1 clays ; 71.3.1b Smectite group (Trioctahedral Smectites)
High temperature:
Low temperature mineral. At higher temperatures(> 500C), detachment of (OH) ions takes place.
Geological context:
Montmorillonite and beidellite are the principal constituents of bentonite clay deposits. Montmorillonite results from the weathering of basic rocks mainly in conditionsof poordrainage when magnesium is not removed.
Dernière mise à jour le 25.01.2021